The dividend yield can be calculated from the last full year’s financial report. Alternatively, investors can also add the last four quarters of dividends, which captures the trailing 12 months of dividend data. Using a trailing dividend number is acceptable, but it can make the yield too high or too low if the dividend has recently been cut or raised.
Which Stock Has the Highest Dividend Yield?
These sites often report trailing dividend yields, and sometimes they still show a yield that’s no longer accurate even after a company has announced a dividend cut. Value investors consider a high dividend yield ratio as a strong value indicator. If a quality stock is yielding a high dividend, then it is considered as undervalued. Improvement of sales and profit figures are one of the strongest fundamental indicators of quality stocks. An ideal situation from an investor’s perspective will be high profitability and low debt. Normally, in developing countries, such a situation is not easily available, and most companies are keen on leveraging the high amount of debts on their balance sheets.
How do your choose dividend stock companies?
If a stock’s dividend yield isn’t listed as a percentage or you’d like to calculate the most-up-to-date dividend yield percentage, use the dividend yield formula. To calculate dividend yield, all you have to do is divide the annual dividends paid per share by the price per share. Companies that generate consistent and stable profits may be more likely to pay regular dividends. In contrast, companies in high-growth phases may prefer to reinvest profits back into the business rather than distribute them to shareholders. The dividend policy can therefore provide insights into a company’s financial health and management’s confidence in future earnings.
How Does Dividend Yield Differ From Dividends?
It is to be noted that in the face of the situation, the yield may appear to attract dividend investors; it is a value trap. A firm that shows a stock price falling from $50 to $20 is perhaps struggling, and one should make a detailed analysis before considering a plunge in the stocks. Dividend yields change and have an inverse relationship to the stock price. The yield rises when the price of the stock falls and falls when the price of the stock rises.
- A regularly increasing dividend is an indication of earnings growth and typically a good indicator of a company’s overall financial health.
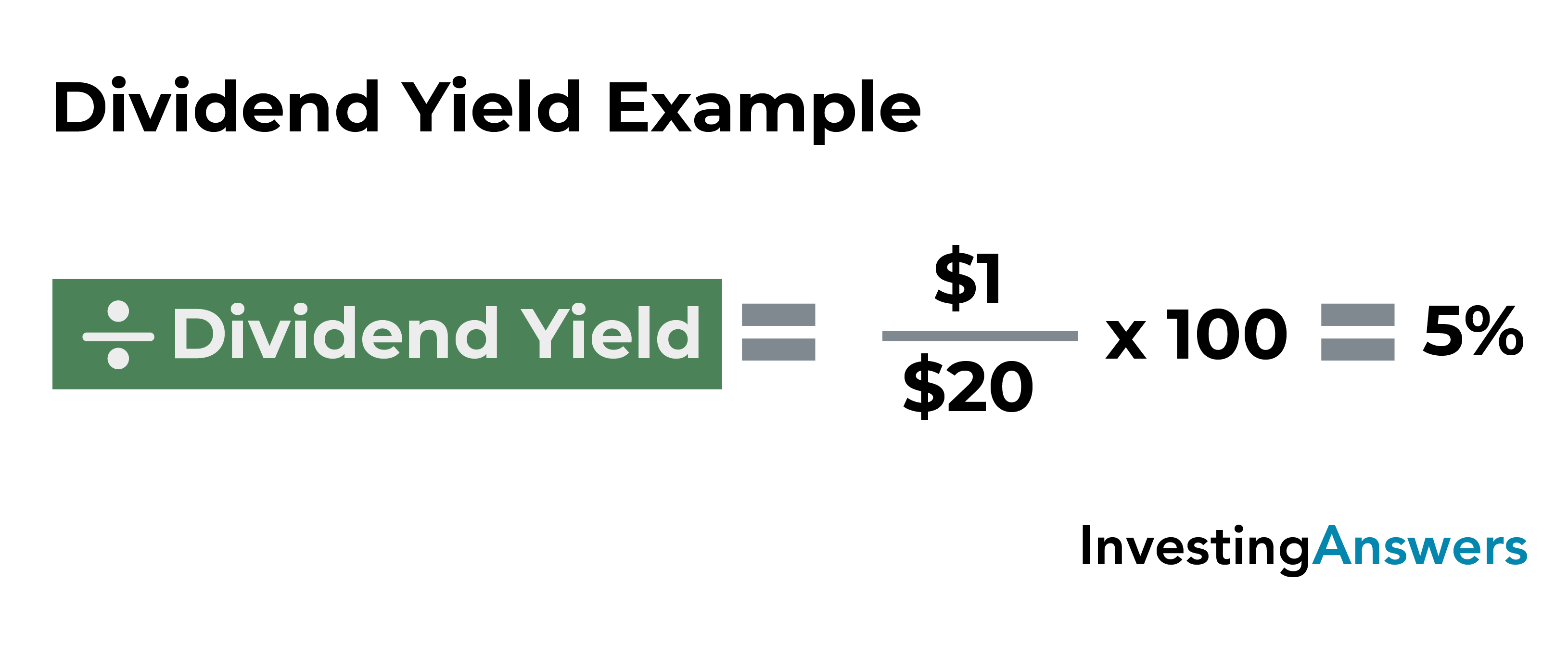
- The formula for calculating the dividend yield is equal to the dividend per share (DPS) divided by the current share price.
- This makes it easier to see how much return the shareholder can expect to receive per dollar they have invested.
- Depending on your investing goals, you could be skipping the best dividend stocks if you’re focusing too closely on dividend yield.
- For other investors, dividend yield may be less significant, such as for younger investors who are more interested in growth companies that can retain their earnings and use them to finance their growth.
We have prepared this document to help you understand what dividend yield is and how to calculate dividend yield. We will also demonstrate some examples to charitable tax deductions help you understand what a good dividend yield is. Compounding is when you reinvest the money earned from your investment back into the initial investment.

Using the MarketBeat Dividend Yield Calculator
Dividend yield allows you to compare the dividend payments of different companies and better evaluate them as investments. This is especially important for income investors, who look for a constant stream of earnings from their stock market holdings. The difference between this straight-up dollar amount and a company’s dividend yield is that the latter is a ratio. The dividend yield is the company’s annual dividend divided by the current stock price, and expressed as a percentage. A stock’s dividend yield is how much the company annually pays out in dividends to shareholders, relative to its stock price. The dividend yield is a financial ratio (dividend/price) expressed as a percentage, and is distinct from the dividend itself.
High-dividend stocks can also offer the benefit of compounding returns if dividends are reinvested. Dividend yield shows how much a company pays its shareholders in dividends annually per dollar invested. It reflects how much an investor will earn aside from any capital gains in the stock. As noted earlier, a dividend is a way for a company to distribute some of its earnings among shareholders.
It is equally critical to reinvest dividend that flows in as this excess money can be used for purchasing more dividend stocks which are cyclical in nature. More stocks mean more dividends, which again is used for buying more stocks. There will be fewer buyers for dividend-yielding scripts than sellers as they are more lucrative. During scenarios of a crash, the market price of stocks tends to fall, but such dividend stocks will want to stand tall in the market by offering a reasonable amount of dividends. Investors will prefer to buy dividend-yielding stocks during a stock market slump to their portfolios.
