ROI is the better-known measurement and is more commonly used than IRR, which is more difficult to calculate. Another advantage of using this rule is that it helps companies and investors account for the time value of money (TVM). This is a concept that states that a particular amount of money is worth more now than the same sum in the future.

What Is Internal Rate of Return (IRR) And How Is It Calculated?
Big-Is-Best requires a capital investment of 100,000 US dollars today, and the lucky investor will be repaid 132,000 US dollars in a year’s time. Small-Is-Beautiful only requires 10,000 US dollars capital to be invested today, and will repay the investor 13,750 US dollars in a year’s time. When the objective is to maximize total value, the calculated IRR should not be used to choose between mutually exclusive projects. Another problem with using the IRR to evaluate a project is that it assumes that any and all interest payments or dividends are reinvested in the project. However, the company making the investment may want to take these dividends and pay them to the shareholders instead of reinvesting them.
IRR Vs NPV
“Once the IRR is obtained, it’s compared to the hurdle rate in order to determine if the project is viable,” Garza says. “If the IRR is higher than the hurdle rate, then the project adds value.” Excel does all the necessary work for you, arriving at the discount rate you are seeking to find. If the net present value of a project or investment is negative, then it is not worth undertaking, as it will be worth less in the future than it is today.
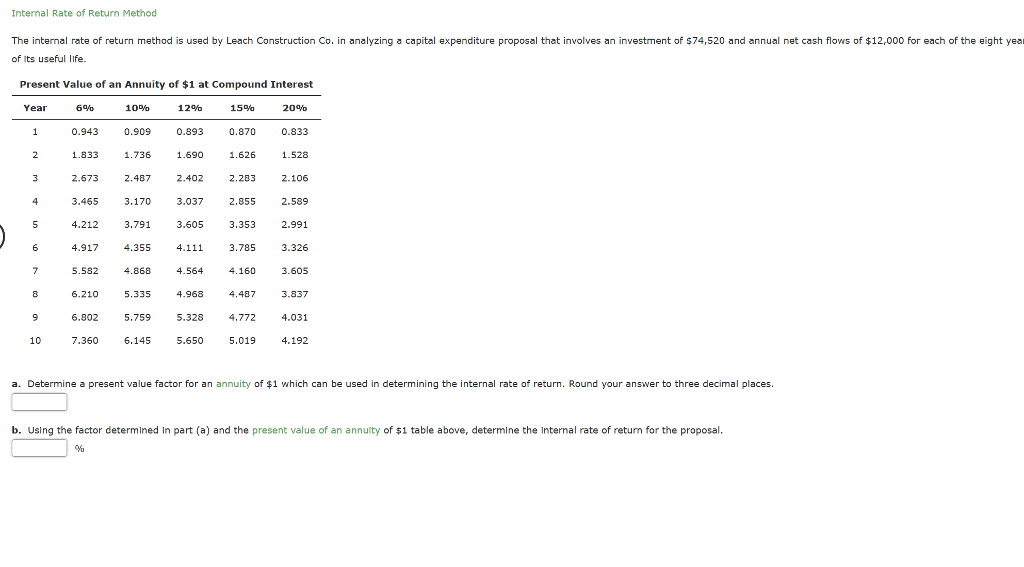
Calculation For IRR
Here, our assumption is that exit proceeds increase by a fixed amount of $25 million each year, starting from the initial investment amount of $85 million. The value of the initial investment stays unchanged regardless of which year the firm exits the investment. Regardless, the internal rate of return (IRR) and MoM are both different pieces of the same puzzle, and each comes with its respective shortcomings.
An Example of an IRR Calculation
- The IRR is the discount rate that can bring an investment’s NPV to zero.
- Finance Strategists has an advertising relationship with some of the companies included on this website.
- In capital planning, one popular scenario for IRR is comparing the profitability of establishing new operations with that of expanding existing operations.
- If market conditions change over the years, this project can have multiple IRRs.
- They provide essential perspectives on project performances and helps in focusing on the profit targets by taking into account the time value of money.
- This particular drawback is overcome by using the modern methods of determining IRR.
The IRR is the discount rate at which the net present value (NPV) of future cash flows from an investment is equal to zero. Functionally, the IRR is used by investors and businesses to find out if an investment is a good use of their money. An economist might say that it helps identify investment opportunity costs.
The answer lies in the fact that the investors do not have to invest the full 100,000 US dollars. After all, Max Return may rationalize the outcome by thinking that maybe tomorrow there will be new opportunities available to invest the remaining 90,000 US dollars the bank is willing to lend Max Return, at even higher IRRs. Max Value is also happy, because she has filled her capital budget straight away, and decides she can take the rest of the year off investing. Investors Max Value and Max Return are presented with two possible projects to invest in, called Big-Is-Best and Small-Is-Beautiful.
For this reason, many investors use the Modified Internal Rate of Return, or MIRR, which accounts for these assumptions. For this reason, many investors use the Modified Internal Rate of Return, or MIRR, which account for these assumptions. If applied iteratively, either the secant method or the improved formula always converges to the correct solution.
As such, it might favor smaller projects with higher returns over larger projects with lower returns but higher net cash flows. They also assume that all cash inflows earned during the project life are reinvested at determining basis for gambling losses the same rate as IRR. These two issues are accounted for in the modified internal rate of return (MIRR). However, using IRR to sort projects in order of preference does not result in the same order as using NPV.
If there were a project that JKL could undertake with a higher IRR, it would probably pursue the higher-yielding project instead. The IRR uses cash flows (not profits) and more specifically, relevant cash flows for a project. To perform the calculation, we need to take the cash flows of a project and calculate the discount factor that would produce a NPV of zero. From Year 0 to Year 1, the sign changed once (negative cash flow of -$100,000 to a positive cash flow of $52,000.
