The bookkeepers or accountants of a business usually maintain the general journal. The general journal entry records the business’s financial transactions in order by date. Accounting journals are often called the book of first entry because this is where journal entries are made. Once a business transaction is made, the bookkeeper records that event in the form of a journal entry in one of the accounting journals.
How Liam Passed His CPA Exams by Tweaking His Study Process
However, the sum of the debits must always be equal to the sum of the credits. When making an entry you must always debit the receiver and credit the giver. Also, you have to debit all expenses and losses and credit all incomes and gains. The next columns that come after the Post Ref column are the Debit and Credit columns, with the credited account being placed one row below the debited account.
To Ensure One Vote Per Person, Please Include the Following Info
- Thus, the general journal can be considered an intermediate repository of information for some types of information, on the way to its final recordation in the general ledger.
- Each type has specific uses but all of them are considered books of original entry since they serve as initial records of transactions that enter into the accounting system.
- A brief description known as narration is also written in this column below the credit part of the entry.
- Following these steps ensures that entries are recorded accurately and efficiently.
- One of our specialists will get in touch with you to set up a live demo.
Please take a moment to submit your information by clicking the button below. One of our specialists will get in touch with you to set up a live demo. Equip yourself with the right tools and resources from our shop, or explore our free accounting lessons. Entry #14 — PGS has more cash sales of $25,000 with cost of goods of $10,000.
Debit and Credit columns
In addition, they may also be used to show transactions that have been recorded in a general journal or some other type of specialized book of accounts. With the advent of technology, record keeping has been easy, with all the information being stored in a single repository with no specialty journals in use. However, these general journal accounting were more visible in the manual record-keeping days. It is different from the specialized journals like sales, purchase etc, where only items related to them are recorded. It mainly keeps the details of five major accounting heads which are assets, liabilities, revenue, expense and capital. The description of the transaction assists bookkeepers and accountants to recall what exactly happened on a certain date or why a transaction occurred.
Do you already work with a financial advisor?
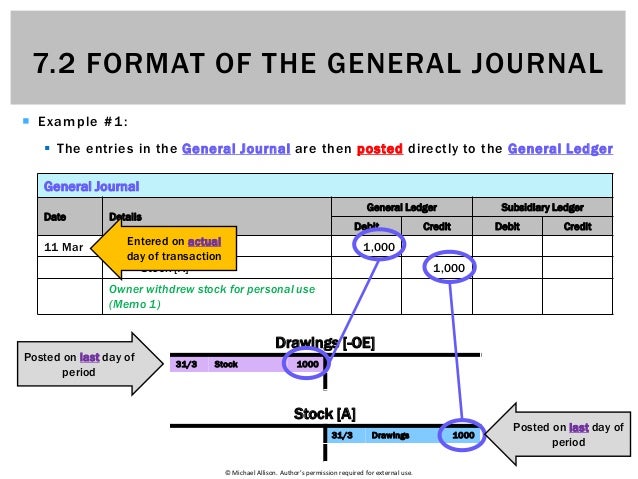
The debit part of the entry is written first and the credit part is written below the debit part. Examples include a sales or purchase return, a compound entry involving several accounts, and most adjusting entries. The first step is transaction analysis, which provides the information needed to journalize a transaction. The general journal will give a chronological record of all non-specialized entries that are otherwise recorded in one of the specific journals. Entries in the general journal play a vital role in the accounting process. By understanding how to record these entries accurately and regularly reviewing them, businesses can maintain their financial integrity and make informed decisions based on reliable data.
The first book in which transactions are recorded is called the general journal. Transactions are recorded in chronological order (i.e., the order of their occurrence). The journal, also known as the general journal, is involved in the first phase of accounting because all transactions are recorded in it, originally in chronological order. Your company probably has transactions that are repetitive and occur more frequently, such as sales and purchase transactions. While you may use the general journal to record these transactions, it could be cumbersome and sometimes result in a cluttered journal and a slow recording process prone to errors. With the advent of computerized accounting systems, the use of physical books of accounts was virtually eliminated.
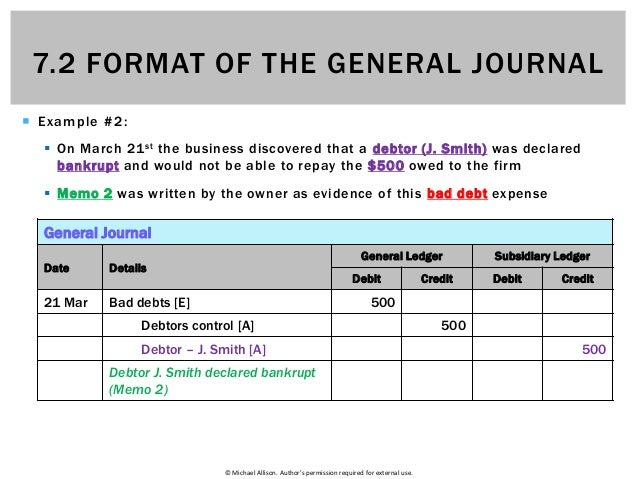
For instance, a description for a general journal may be written as ‘To record equipment purchase‘ or ‘To record inventory payment’. Recording a transaction in the books of accounts is known as making an entry. When a transaction is recorded in the journal, it is known as a journal entry.
A general journal is a chronological accounting record of a company’s financial transactions. The main purpose of this is to assist in the reconciliation of accounts and to assist with producing financial statements. General journals are also known as an “individual journal” or “book of original entry.” These records may contain information about cash receipts and payments. The general journal is part of the accounting record keeping system. When an event occurs that must be recorded, it is called a transaction, and may be recorded in a specialty journal or in the general journal. There are four specialty journals, which are so named because specific types of routine transactions are recorded in them.
Journal entries are the first step in the accounting cycle and are used to record all business transactions and events in the accounting system. As business events occur throughout the accounting period, journal entries are recorded in the the issuance of common stock general journal to show how the event changed in the accounting equation. For example, when the company spends cash to purchase a new vehicle, the cash account is decreased or credited and the vehicle account is increased or debited.
